package com.vaannila.student;02. 03.// Generated May 30, 2009 6:48:40 AM by Hibernate Tools 3.2.4.GA04. 05./**06.* This class contains the course details.07.* 08.*/09.public class Course implements java.io.Serializable {10. 11.private long courseId;12.private String courseName;13. 14.public Course() {15.}16. 17.public Course(String courseName) {18.this.courseName = courseName;19.}20. 21.public long getCourseId() {22.return this.courseId;23.}24. 25.public void setCourseId(long courseId) {26.this.courseId = courseId;27.}28. 29.public String getCourseName() {30.return this.courseName;31.}32. 33.public void setCourseName(String courseName) {34.this.courseName = courseName;35.}36. 37.}01.package com.vaannila.student;02. 03.import java.util.HashSet;04.import java.util.Set;05. 06.import org.hibernate.HibernateException;07.import org.hibernate.Session;08.import org.hibernate.Transaction;09. 10.import com.vaannila.util.HibernateUtil;11. 12.public class Main {13. 14.public static void main(String[] args) {15. 16.Session session = HibernateUtil.getSessionFactory().openSession();17.Transaction transaction = null;18.try {19.transaction = session.beginTransaction();20. 21.Set<Course> courses = new HashSet<Course>();22.courses.add(new Course("Maths"));23.courses.add(new Course("Computer Science"));24. 25.Student student1 = new Student("Eswar", courses);26.Student student2 = new Student("Joe", courses);27.session.save(student1);28.session.save(student2);29. 30.transaction.commit();31.} catch (HibernateException e) {32.transaction.rollback();33.e.printStackTrace();34.} finally {35.session.close();36.}37. 38.}39.}
Create the Main class to run the example.
01.package com.vaannila.student;02. 03.import java.util.HashSet;04.import java.util.Set;05. 06.import org.hibernate.HibernateException;07.import org.hibernate.Session;08.import org.hibernate.Transaction;09. 10.import com.vaannila.util.HibernateUtil;11. 12.public class Main {13. 14.public static void main(String[] args) {15. 16.Session session = HibernateUtil.getSessionFactory().openSession();17.Transaction transaction = null;18.try {19.transaction = session.beginTransaction();20. 21.Set<Course> courses = new HashSet<Course>();22.courses.add(new Course("Maths"));23.courses.add(new Course("Computer Science"));24. 25.Student student1 = new Student("Eswar", courses);26.Student student2 = new Student("Joe", courses);27.session.save(student1);28.session.save(student2);29. 30.transaction.commit();31.} catch (HibernateException e) {32.transaction.rollback();33.e.printStackTrace();34.} finally {35.session.close();36.}37. 38.}39.}
On executing the Main class you will see the following output.
The STUDENT table has two records.
The COURSE table has two records.
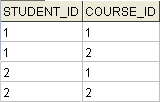
The STUDENT_COURSE table has four records to link the student and courses.
Each student has enrolled in the same two courses, this illustrates the many-to-many mapping.
The folder structure of the example is shown below.




No comments:
Post a Comment