In this example you will learn how to map many-to-many relationship using Hibernate Annotations. Consider the following relationship between Student and Course entity.
According to the relationship a student can enroll in any number of courses and the course can have any number of students.
To create this relationship you need to have a STUDENT, COURSE and STUDENT_COURSE table. The relational model is shown below.
To create the STUDENT, COURSE and STUDENT_COURSE table you need to create the following Java Class files.
Student class is used to create the STUDENT and STUDENT_COURSE table.
01.package com.vaannila.student;02. 03.import java.util.HashSet;04.import java.util.Set;05. 06.import javax.persistence.CascadeType;07.import javax.persistence.Column;08.import javax.persistence.Entity;09.import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue;10.import javax.persistence.Id;11.import javax.persistence.JoinColumn;12.import javax.persistence.JoinTable;13.import javax.persistence.ManyToMany;14.import javax.persistence.Table;15. 16.@Entity17.@Table(name = "STUDENT")18.public class Student {19. 20.private long studentId;21.private String studentName;22.private Set<Course> courses = new HashSet<Course>(0);23. 24.public Student() {25.}26. 27.public Student(String studentName) {28.this.studentName = studentName;29.}30. 31.public Student(String studentName, Set<Course> courses) {32.this.studentName = studentName;33.this.courses = courses;34.}35. 36.@Id37.@GeneratedValue38.@Column(name = "STUDENT_ID")39.public long getStudentId() {40.return this.studentId;41.}42. 43.public void setStudentId(long studentId) {44.this.studentId = studentId;45.}46. 47.@Column(name = "STUDENT_NAME", nullable = false, length = 100)48.public String getStudentName() {49.return this.studentName;50.}51. 52.public void setStudentName(String studentName) {53.this.studentName = studentName;54.}55. 56.@ManyToMany(cascade = CascadeType.ALL)57.@JoinTable(name = "STUDENT_COURSE", joinColumns = { @JoinColumn(name ="STUDENT_ID") }, inverseJoinColumns = { @JoinColumn(name ="COURSE_ID") })58.public Set<Course> getCourses() {59.return this.courses;60.}61. 62.public void setCourses(Set<Course> courses) {63.this.courses = courses;64.}65. 66.}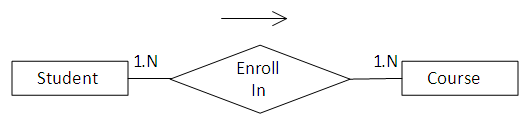


No comments:
Post a Comment